Reassessing the Role of Antioxidant Supplements in Male Fertility
The latest clinical trial findings have stirred conversation in the fertility care community. A large, multicenter randomized trial, known as the SUMMER study, set out to assess if the antioxidant supplement Impryl could boost male fertility. In a surprising turn, the study revealed that not only did Impryl fail to improve pregnancy rates compared to a placebo, but during a critical treatment window its use was even associated with lower pregnancy outcomes.
These findings underscore the need to carefully scrutinize popular health products, especially when they promise to address tricky parts of complex biological processes. As a healthcare professional and committed observer of modern research, I invite you to join me as we dig into the details of this study, examine the underlying mechanisms, and consider the practical implications for those navigating the tangled issues surrounding male infertility.
Unpacking the SUMMER Trial Findings
The SUMMER trial, conducted in the Netherlands across 21 hospitals and fertility clinics between 2018 and 2024, stands as one of the largest investigations into the efficacy of antioxidant supplements in treating male infertility. Over 1,170 men aged 18 to 50, all seeking fertility support via techniques such as intrauterine insemination, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), or in vitro fertilization (IVF), participated by being randomly assigned either to an antioxidant supplementation group or a placebo group.
The supplement in question, Impryl, is comprised of several components that have been touted for male reproductive health. These include betaine, L-cystine, niacin, zinc, vitamin B6, vitamin B2, folic acid, and vitamin B12. Despite the promising combination of these ingredients, after six months of supplementation, the overall ongoing pregnancy rate did not improve. In fact, during the window from 4 to 6 months—when the treatment would be expected to have its optimal effect—the results in the antioxidant group were notably lower than in the placebo group.
This early release of results was prompted by concerns regarding a potential adverse effect associated with antioxidant treatment, urging us to take a closer look at commonly held assumptions about over-the-counter supplements in fertility care.
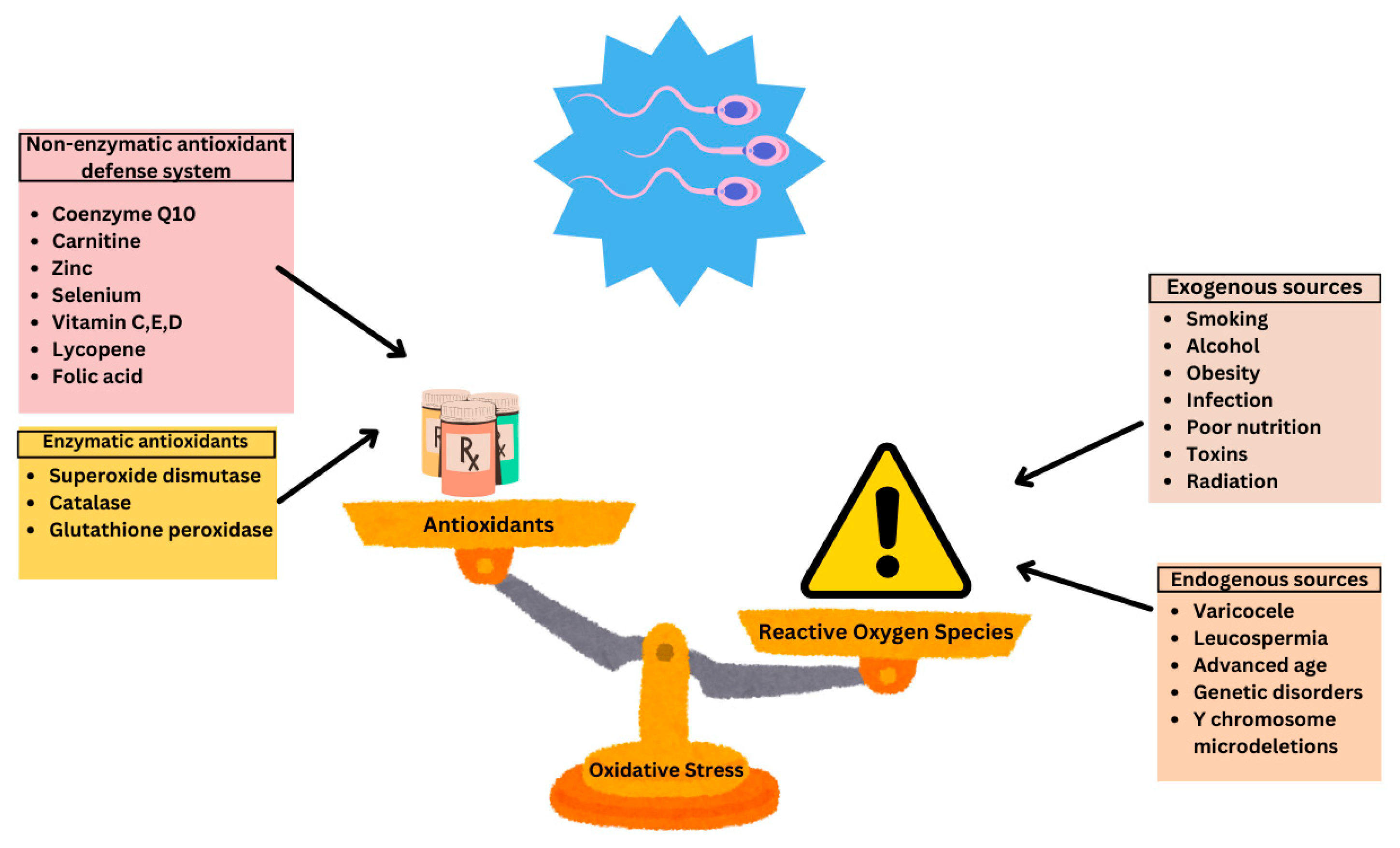
What Does Oxidative Stress Mean for Male Fertility?
Oxidative stress occurs when the body’s natural balance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants is disrupted. ROS are molecules produced during normal cell functions, but when they become excessive, they can damage DNA and sperm membranes. Many believe that by supplementing antioxidants, one can neutralize these harmful molecules, thus improving sperm quality.
However, there is a twist: while moderate antioxidant levels are indeed essential, too much can trigger what is known as reductive stress—a state where the balance is shifted too far in the opposite direction. This can potentially harm sperm vitality. In the case of Impryl, the anticipated benefit was to counteract the delicate balance between ROS and antioxidant defenses. Yet, the study’s findings suggest that this balance might be more easily upset than previously thought.
- Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) – Molecules that can damage sperm and DNA
- Antioxidants – Compounds meant to counteract the negative effects of ROS
- Reductive Stress – A condition caused by excessive antioxidant intervention that may impair normal cellular functions
This discovery challenges many traditional beliefs and calls for a deeper exploration of the subtle parts influencing male reproductive health.
Understanding the Critical Treatment Window in Fertility Care
One of the most significant observations from the study was the difference in pregnancy rates during the treatment’s optimal window, particularly from four to six months. This period corresponds with the 72-day cycle required for sperm production—a cycle that is both fascinating and complex in its own right.
It is during this time that the interventions, either beneficial or counterproductive, can have their most pronounced effects on fertility outcomes. The fact that using Impryl during this crucial interval was linked with a significant drop in pregnancy success raises red flags. It suggests that even well-meaning supplement regimens can have unintended, even counterproductive outcomes, if the timing and dosing are not meticulously calibrated.
For those trying to find their way through the many options presented by modern fertility treatments, this serves as a reminder that the timing of intervention is super important, and understanding these critical periods can help avoid potentially nerve-racking pitfalls.
Ingredients at a Closer Glance: What Exactly Is in Impryl?
Impryl is formulated with a blend of antioxidant compounds aimed at boosting fertility. Let’s break down these ingredients and assess their individual roles:
- Betaine (200 mg): Often highlighted for its role in reducing homocysteine levels, which in turn can help improve sperm health.
- L-cystine (200 mg): An amino acid that is believed to contribute to the synthesis of glutathione, a key antioxidant.
- Niacin (16 mg): A form of vitamin B3 that supports energy metabolism and overall cell function.
- Zinc (10 mg): Critical for proper immune function and reproductive health, with known implications in supporting sperm concentration and motility.
- Vitamin B6 (1.4 mg) and Vitamin B2 (1.4 mg): Both play roles in cellular energy production, which is essential when cells are under oxidative attack.
- Folic Acid (400 μg): Widely recognized for its role in DNA synthesis and repair.
- Vitamin B12 (2.5 μg): Important for proper neurological function and DNA production.
While each of these components has its inherent merit and has been linked in some studies to improved reproductive functions, their combination in a setting that is already loaded with intricate hormonal and cellular processes appears to have a double-edged outcome. When taken over time, the overall effect may disrupt rather than support the subtle details of sperm maturation.
Data-Driven Insights: Comparing Placebo and Antioxidant Groups
An objective look at the data is essential to understand this study’s outcome. After six months, ongoing pregnancy rates were 33.8% for the antioxidant group versus 37.5% for the placebo group. More striking, during the optimal window for treatment, the pregnancy rate in the antioxidant group dropped to 15.5% compared to 21.5% in the placebo cohort.
Presented in tabular form, here’s a simplified comparison:
| Parameter | Antioxidant Group | Placebo Group |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Ongoing Pregnancy Rate | 33.8% | 37.5% |
| Pregnancy Rate during 4-6 Month Window | 15.5% | 21.5% |
While the differences might seem subtle when translated into percentages, the data clearly suggest that the antioxidant supplement did not deliver the anticipated boost—and may have inadvertently created complications when used during a pivotal phase of sperm production.
Implications for Assisted Reproductive Technologies
In today’s fertility clinics, many couples turn to assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as IVF and ICSI in the hope of overcoming conception hurdles. Within the same study, a noteworthy trend was observed in these subgroups: couples undergoing IVF or ICSI who used the antioxidant supplement experienced lower pregnancy outcomes during fresh embryo transfers, while frozen-thawed embryo transfers were not significantly affected.
This discrepancy raises a couple of key points to consider:
- The effect of antioxidants might be more pronounced in conditions where immediate sperm and embryo dynamics are critical.
- The environment of a fresh embryo transfer could be more sensitive to subtle shifts in sperm quality or vitality compared to frozen cycles.
As physicians and patients work together to figure a path through the maze of fertility treatment options, understanding the tiny details of how supplements interact with ART protocols becomes essential. This knowledge may pave the way to more tailored, individualized treatment regimens that do not rely solely on over-the-counter supplements whose effects are still under debate.
Digging into the Potential Mechanisms Behind the Disappointing Outcomes
There are several plausible reasons why antioxidant supplementation might backfire when it comes to improving male fertility. Here are some of the possible explanations, broken down into simpler terms:
- Disruption of the Oxidative Balance: In a healthy system, a balance exists between ROS production and antioxidant defenses. Over-supplementation may tip the scale too far, leading to reductive stress that can actually impair sperm function.
- Interference with Essential Cellular Signaling: Some level of ROS is necessary for proper cell signaling and normal sperm maturation. Excessive antioxidant presence might interfere with these fine shades of communication.
- Individual Variability: Every man’s physiology is different. The same dose of an antioxidant may have various effects depending on underlying health conditions, baseline oxidative stress levels, or even genetic predispositions.
Ultimately, while the theory behind using antioxidants is appealing, the actual biological environment in the human body is filled with complicated pieces and nerve-racking twists and turns. More research is needed to understand how best to support the reproductive process without inadvertently causing harm.
Community Reactions and Future Directions in Fertility Care
The broader fertility and medical research communities have reacted with a mix of surprise and caution to these findings. Several experts have voiced concern over the widespread use of such supplements without robust clinical backing. Many argue that in an era where evidence-based practices are crucial, it is not enough to rely on theoretical benefits.
Looking ahead, what are the key takeaways for the future?
- Need for Larger, More Focused Trials: Despite the size of the SUMMER trial, there remain many subtle parts in the fertility puzzle that are not fully understood. Future research could target specific subgroups, such as those with known oxidative imbalances.
- Personalized Medical Approaches: Rather than a one-size-fits-all approach, personalized evaluations could determine who might actually benefit from antioxidant supplementation.
- Reevaluating Supplement Protocols: The current findings suggest that clinicians and patients alike should think twice before routinely using such supplements, especially during critical treatment windows.
For those who are managing their way through fertility challenges and exploring various treatment options, these results emphasize the value of staying informed and relying on robust clinical evidence over marketing claims.
Practical Takeaways for Men Considering Fertility Supplements
The disappointment in the study findings is certainly a mixed bag of emotions for men and couples who have placed their hopes in antioxidant supplements. While it is important not to disregard the potential benefits entirely, caution is warranted. Here are some practical steps and reminders:
- Consultation with Specialists: Always have an in-depth discussion with a reproductive specialist who can help weigh up the pros and cons based on your individual health profile.
- Examine the Scientific Evidence: Before investing in any supplement, take the time to review current research and, if possible, inquire about ongoing clinical trials that target your specific concerns.
- Consider a Holistic Approach: Often, fertility challenges are not due to a single issue but arise from a combination of lifestyle, nutrition, and underlying health conditions. A comprehensive approach that includes diet adjustments, exercise, and stress management might be more beneficial.
- Stay Current on Research: Science evolves, and what seems ineffective today could be revisited with new protocols and formulations in the future. Keeping up with reputable health news sources and consulting professionals can help steer you safely through the evolving landscape.
While the allure of a simple antiseptic solution like an over-the-counter supplement is tempting, the realities of human biology demand that we pay close attention to the subtle details that come into play. It is critical to be aware that what may work as a theory does not always translate neatly into real-world success.
Finding Your Path through a Confusing World of Fertility Treatments
The journey toward parenthood can be filled with confusing bits and overwhelming options. With countless products and methods promising everything from improved vitality to enhanced pregnancy rates, it is easy to get tangled up in the twists and turns of modern fertility marketing. The story of Impryl is a clear signal that not all that glitters is gold.
When making decisions about your health, especially in a field as complicated as fertility, it is essential to figure a path anchored in evidence. The latest trial results remind us that marketing claims should always be taken with a grain of salt, regardless of how promising the ingredients might look on paper.
For those navigating the nerve-racking realm of fertility treatments, the key is to maintain a balanced perspective and rely on the guidance of trusted medical experts. Soon or later, treatments that work for one individual may not apply universally, and it is important to keep this reality in mind during your decision-making process.
Revisiting the Balance: Risks versus Benefits of Supplementation
An integral part of this discussion revolves around risk versus benefit. Clinicians must balance potential benefits with the possible risks that come from interfering with the body’s natural processes. The SUMMER trial cast doubt on whether antioxidant supplementation is as beneficial as once hoped. With evidence pointing toward possible reductions in key fertility outcomes, the routine use of such supplements becomes something to be approached with caution.
Consider the following points when making your judgment:
- Risk of Reductive Stress: Over-supplementation can lead to an imbalance that may be as problematic as the oxidative stress it was intended to combat.
- Potential Impact on Sperm Vitality: While traditional markers like volume and concentration remained largely unchanged, aspects such as sperm vitality showed negative trends when antioxidants were used.
- Importance of Precise Timing: The study made it evident that the period of supplementation is critical; indiscriminate use during sensitive periods may lead to unintended outcomes.
In a field where every percentage point counts, these findings diverge from the expectations set by previous, smaller studies. They serve as a cautionary tale to both patients and clinicians, guiding them to proceed with extra care when considering any intervention that interferes with the body’s delicate balance.
The Bigger Picture: Why Evidence-Based Decisions Matter
In our fast-paced world, where new treatments and supplements hit the market regularly, the importance of evidence-based decision-making cannot be overstated. The disappointing outcomes of the antioxidant trial are a reminder that clinical success hinges on well-designed, large-scale studies rather than anecdotal successes or marketing hype.
Here are a few ways in which robust clinical evidence benefits the entire fertility care community:
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Rigorous trials help identify not only the positives but also any unintended consequences, ensuring that patients are not inadvertently exposed to harmful side effects.
- Clearer Guidance for Clinicians: Doctors can better tailor treatments when they have access to high-quality, evidence-backed research that highlights both benefits and risks.
- Targeted Research for Future Innovations: Recognizing where current methods fall short opens up avenues for innovative treatments that can handle the tricky parts of human biology more effectively.
With the growing popularity of self-prescribed supplements and an increasingly competitive market, the need for well-conducted clinical trials must be a top priority. The SUMMER trial is a wake-up call, urging the medical community to invest in more nuanced studies that clearly define which treatments work and which do not.
Final Thoughts: Navigating a Complex Landscape with Caution
As we take a closer look at the evolving narrative of male fertility treatments, a few key points stand out. The evidence from the SUMMER trial indicates that antioxidant supplementation, as implemented in the study, does not improve—and might even compromise—fertility outcomes during a key period of sperm production.
For patients, the story is a reminder that clear, evidence-based guidance is paramount. Before embarking on any supplementation regimen, particularly one that promises quick fixes or miraculous outcomes, consider these reminders:
- Always talk to your healthcare provider about any changes in your treatment plan.
- Rely on data from robust, peer-reviewed studies rather than solely on marketing claims.
- Keep in mind that what works in theory does not always bear fruit in practice.
- Be open to alternative strategies that incorporate a comprehensive approach to overall health and fertility.
In the world of healthcare and fertility, making your way through the maze of available treatments can be intimidating. Yet, by leaning on scientific evidence, asking the right questions, and understanding the little twists that make each individual’s situation unique, patients and clinicians alike can work together towards more effective, personalized care.
Looking Ahead: The Need for Tailored Fertility Support
The results of this trial not only cast doubt on the benefits of a widely marketed antioxidant supplement but also highlight the broader challenge of creating one-size-fits-all solutions in fertility care. The findings serve as a catalyst for rethinking current supplementation practices and point towards a future where treatment is more precisely tailored to an individual’s unique biology.
As research continues, it will be essential to further explore:
- How individual variability affects response to supplementation, ensuring that treatments can be personalized rather than broadly applied.
- The role of lifestyle and nutritional factors in modulating oxidative balances and overall reproductive health.
- The interaction between antioxidant supplements and assisted reproductive technologies, particularly in timing and dosing strategies.
New studies might pave the way for combination therapies, where antioxidants are used in conjunction with other, supportive treatments. These may include dietary interventions, targeted exercise regimens, and even stress-management techniques—methods that collectively enhance overall health rather than relying on a single supplement to serve as a magic bullet.
Conclusion: Staying Informed and Cautious for Better Outcomes
The SUMMER trial provides us with a sobering look into the challenges faced by the medical community when trying to address male infertility with supplements. While antioxidant supplements like Impryl have been embraced by many for their theoretical benefits, the actual impact on fertility outcomes in a large, real-world clinical setting does not match the promise often marketed to consumers.
For those who are sorting out the various treatment options available today, the key takeaway is to remain cautious. Engage in informed discussions with healthcare professionals, examine the evidence carefully, and always consider both the potential benefits and the risks involved. After all, when dealing with something as personal and essential as fertility, the stakes are high and the consequences of misguided interventions can be significant.
In conclusion, while the journey to parenthood is filled with many nerve-racking and sometimes overwhelming decisions, grounding those decisions in robust, evidence-based research will always be a super important strategy. Let the findings from studies like the SUMMER trial guide not only the future of fertility treatments but also our broader approach to managing the challenging parts of modern medicine.
Originally Post From https://www.news-medical.net/news/20250928/Clinical-trial-disproves-claims-that-antioxidant-supplement-boost-male-fertility.aspx
Read more about this topic at
Watch Out for False Promises on Some Dietary Supplements
Don’t waste time (or money) on dietary supplements
