Introduction: A Rare Medical Conundrum in Modern Oncology
The realm of modern medicine is filled with both breakthroughs and unexpected challenges. One such challenge arises when clinicians encounter extremely rare conditions that blur the lines between benign disorders and malignant cancers. A recent case involving a 54-year-old male who presented with persistent chest pain has highlighted the tricky parts of diagnosing oesophageal lesions, particularly when they mimic more common malignancies. This opinion editorial explores the subtle details and tangled issues associated with diagnosing and treating Castleman’s disease in the oesophageal region, and emphasizes the importance of multidisciplinary collaboration and complete surgical intervention as the key to restoring patient health.
Castleman’s disease (CD) is a benign lymphoproliferative disorder whose underlying causes remain uncertain. When the disorder appears in the oesophageal area—a location where it is exceedingly rare—it can easily be mistaken for oesophageal carcinoma or lymphoma, causing nerve-racking concerns about misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment. In this article, I will take a closer look at the diagnostic dilemma presented by this condition, discussing the role of various imaging techniques, the need for surgical precision, and the broader implications for patient care in both modern and alternative healthcare settings.
Diagnosing Rare Oesophageal Conditions: Untangling the Tricky Parts of Imaging and Biopsy
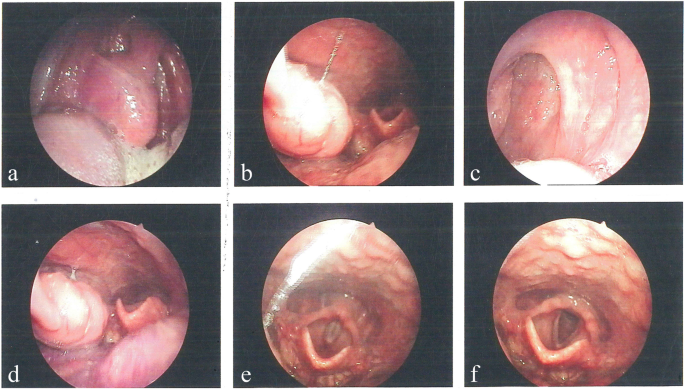
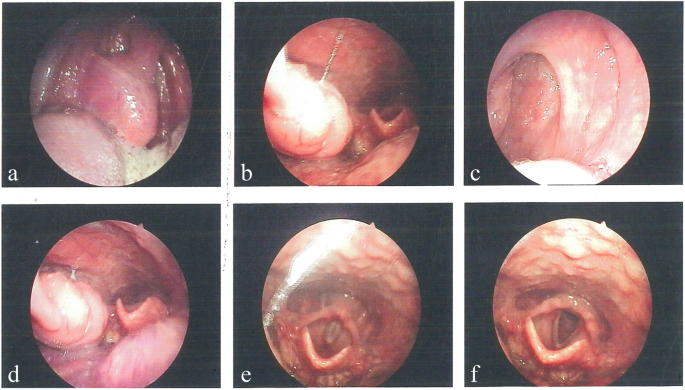
When we look at the diagnostic workflow for unusual conditions, certain imaging methods and tissue sampling techniques become super important. In the case under discussion, several diagnostic tools were put to the test. Conventional barium oesophagography and contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scans revealed stenosis in the lower oesophagus along with wall thickening at the gastroesophageal junction. While these imaging modalities provide critical snapshots of internal anatomy, they sometimes offer confusing bits that can obscure a clear diagnosis.
Positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) further complicated the clinical picture by revealing increased glucose metabolism in both the oesophageal area and nearby lymph nodes. Such findings are typically suspicious for malignancy, but in this case they served to exemplify the fine points of diagnostic complexity. Often, increased metabolic activity is viewed as a red flag pointing to cancer. However, benign conditions like Castleman’s disease can mimic these metabolic patterns, thereby leading clinicians down a nerve-racking path as they try to figure a path through layers of overlapping symptoms.
Alongside imaging, the use of a gastroscopic biopsy was critical. Rather than confirming a cancerous process, the biopsy returned inflammatory granulation tissue without any traces of malignant cells. This discrepancy between radiologic suspicion and pathological findings underscores the challenges physicians face when dealing with such rare and puzzling conditions. The situation calls for a deep dive into diagnostic strategies to ensure that patients are neither over-treated for cancer nor under-treated for potentially malignant lesions.
The Diagnostic Dilemma: When Oesophageal Lesions Mimic Malignancy
The case of Castleman’s disease in the oesophagus is emblematic of the broader challenges experienced in oncology when dealing with unusual presentations. Here we see an example of the overlapping signals that can mislead even the most experienced medical teams. The twists and turns of clinical symptoms and radiological findings demand that doctors remain vigilant and open-minded, always ready to consider rare diagnoses despite feeling overwhelmed by initial impressions.
This diagnostic dilemma is compounded by the fact that many clinicians are more familiar with the common pathways of cancer diagnosis. When encountering increased glucose metabolism on PET-CT—a hallmark of many malignant processes—the instinct is to proceed quickly toward treatment plans designed for cancer. However, in cases like this one, a confirmation via biopsy and eventual surgical exploration revealed an entirely different scenario: a benign yet rare lymphoproliferative disorder.
In several ways, this case reinforces the importance of not letting initial impressions cloud thorough investigation. When faced with confusing bits of evidence, it is critical for clinicians to remain skeptical, dig into all available data, and consider alternative explanations. In doing so, they not only avoid unnecessary aggressive treatments but also reduce the potential for long-term complications that may arise from a misdiagnosis.
Imaging Techniques and Their Role in Unraveling Confusing Cases
The evolution of imaging technology has dramatically improved the accuracy of both diagnosis and surgical planning. However, it has also introduced new layers of twisted issues that require careful interpretation. In the current case, imaging techniques such as CT, PET-CT, and barium oesophagography served as invaluable tools yet presented information that was open to multiple interpretations.
When we examine the role of these imaging modalities, it becomes clear that each test contributes a unique perspective:
- CT Scans: These provided detailed images of the oesophageal wall, showing thickening at the gastroesophageal junction. Although effective in identifying structural abnormalities, CT scans alone are not enough to differentiate between benign and malignant conditions.
- PET-CT: By revealing areas of increased glucose uptake, PET-CT underscored the possibility of malignant processes. However, this case reminds us that increased metabolism is not exclusive to cancers, thereby making it a tricky part in diagnostic evaluation.
- Barium Oesophagography: This technique mapped the anatomical changes and strictures in the oesophagus, offering visual clues about the site of the lesion. Yet, its inability to provide definitive cellular information meant that further investigation was necessary.
The integration of these imaging modalities requires a nuanced approach. When imaging results are riddled with tension and loaded with conflicting signals, it is essential for the clinical team to sort out and weigh each piece of evidence before proceeding with treatment. Ultimately, the combined insights from these tests helped set the stage for the decision to move forward with surgical intervention.
Surgical Intervention: Tackling the Complicated Pieces of Treatment Decisions
Surgical resection in cases of oesophageal lesions is often viewed as the super important step toward a definitive diagnosis and curative treatment. In the discussed case, the decision to perform a partial oesophagectomy with intrathoracic oesophagogastric anastomosis was driven by the need to both manage the patient’s symptoms and to obtain a definitive tissue diagnosis.
The procedure itself was not without its own set of challenges. Surgeons had to make their way through a maze of complicated pieces related to the altered anatomy and potential risks of surgery in the thoracic region. The benefits, however, were significant. With complete resection, not only was the patient relieved of the discomfort and complications linked with the obstructive lesion, but the surgical specimen also allowed for a detailed pathological examination that confirmed the diagnosis of the hyaline vascular type of Castleman’s disease (HV-CD).
This case highlights the dual significance of surgical resection. First, it serves as a critical intervention to alleviate the mechanical issues (such as oesophageal stenosis) associated with the disease. Second, and perhaps more critically, it provides the opportunity for pathologists to inspect the full architecture of the lesion. In this instance, the presence of onion-skin hyperplasia of lymphoid follicles with hyalinized vessels was the fine detail that clinched the diagnosis of HV-CD.
For modern surgical teams, this example reinforces the need for a balanced assessment of when to operate. While non-invasive techniques continue to improve, there remain many scenarios in which surgical exploration is the most reliable route to getting around the confusing bits of ambiguous imaging and inconclusive biopsy results.
Clinical Lessons: Improving Diagnostic Accuracy and Treatment Outcomes
The diagnostic journey in this rare case of oesophageal tumor mimicry is full of lessons that extend well beyond the confines of a single clinical case. For clinicians, researchers, and even patients, there are several key takeaways to consider when faced with rare disorders that present with overlapping symptoms and imaging findings.
One major lesson is the need for a careful and methodical approach, particularly when initial findings are nerve-racking and suggest a high likelihood of malignancy. The following strategies can help in managing such scenarios:
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Always consider the entire clinical picture. Discrepancies between imaging results and biopsy findings should prompt clinicians to seek out additional information or consider alternative diagnoses.
- Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Bringing together experts from radiology, pathology, oncology, and surgery can help figure a path through the maze of confusing evidence. Each specialist offers unique insights that can culminate in a more accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment plan.
- Patient-Centered Decision Making: Informed patients are better equipped to face the reality of their condition. Clear communication regarding the uncertainties and the reasoning behind surgical decisions fosters trust and lowers anxiety over nerve-wracking outcomes.
In these ways, a detailed and cautious approach can ensure that rare but impactful conditions like Castleman’s disease are managed not only efficiently but also with a heightened awareness of the nuanced risks and benefits involved.
Alternative Medicine and Nutritional Perspectives on Unusual Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Modern medicine is not the only lens through which we can examine puzzling conditions; alternative medicine and nutritional strategies also play a role in comprehensive patient care. While surgical resection and advanced imaging are critical for managing the immediate risks associated with Castleman’s disease, supportive measures including holistic nutrition and complementary therapies can help patients recover faster and improve overall wellbeing.
Many patients and advocates for alternative care emphasize the importance of addressing the body’s hidden complexities through diet and lifestyle changes. In cases where long-term inflammation is involved, nutritional support targeted at reducing systemic inflammatory markers may contribute to improved recovery post-surgery. Common recommendations include:
- Anti-inflammatory Diets: Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and other anti-inflammatory components can potentially help manage baseline inflammation.
- Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs and botanical extracts are believed to support immune regulation. However, it is critical to ensure that any supplement taken is discussed with healthcare providers to avoid interactions with conventional treatments.
- Mind-Body Practices: Stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing may contribute to overall recovery by lowering stress hormones, which can, in turn, support immune function.
It is important to stress that while these alternative approaches do not replace conventional treatment, they may serve as valuable adjuncts in a patient’s overall treatment plan. Engaging with both modern and alternative therapies can provide a well-rounded approach to healing, targeting both the physical lesion and the body’s systemic response to disease.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Finding Your Way Through a Tense Healthcare Maze
In the landscape of rare diseases, the benefits of a comprehensive, team-based approach cannot be overstated. When faced with conditions that are on edge with multiple possible interpretations, assembling a team of experts ensures that no stone is left unturned. This collaborative model is one where every member—from radiologists and pathologists to surgeons and nutritionists—plays a super important role.
Consider the following collaborative strategies for managing rare oncological conditions:
- Regular Case Conferences: Multidisciplinary meetings where challenging cases are discussed can help pool expertise and generate innovative solutions. These discussions are particularly useful when initial findings are off-putting and inconsistent.
- Interdepartmental Reviews: Detailed reviews of imaging and biopsy results by multiple departments can help identify subtle details or fine shades that might have been overlooked in standard evaluations.
- Integrated Treatment Plans: A seamless blend of surgical, medical, and supportive therapies ensures a holistic approach to treatment planning, reducing the chance of misdiagnosis and optimizing patient outcomes.
This framework of collaboration not only boosts diagnostic accuracy but also builds in redundancies that are essential when handling rare diseases. By ensuring that each specialist’s insights are valued, the treatment team can steer through the complicated pieces of conflicting evidence and come to a clear, patient-centered decision.
Ongoing Research and the Future Challenges of Rare Oesophageal Disorders
While the case of oesophageal Castleman’s disease offers an in-depth look into the world of rare lymphoproliferative disorders, it also serves as a reminder that many areas of modern oncology are still riddled with tension and loaded with puzzling elements. As we continue to encounter rare conditions, ongoing research is super important to unearth improved diagnostic markers, treatment strategies, and patient support systems.
Medical research in this domain is focusing on several areas including:
- Genetic Profiling: Advanced genetic techniques may help identify predispositions to rare disorders. By understanding the genetic landscape, physicians might one day predict which patients are at risk for developing conditions like Castleman’s disease.
- Immunological Studies: Investigations into the specific immune mechanisms at play could reveal targeted treatments that bypass the need for extensive surgical intervention. This research might offer alternatives for patients who are not ideal candidates for surgery.
- Innovative Imaging Modalities: The development of new imaging techniques with higher precision could help differentiate between benign and malignant processes more effectively, reducing the nerve-racking uncertainty currently associated with PET-CT findings.
These concentrated research efforts are essential to improving our understanding of not only Castleman’s disease but also other rare oncological conditions. As more data is gathered and new diagnostic tools are developed, the hope is that clinicians will be able to make more informed decisions, reducing the reliance on invasive procedures and streamlining treatment pathways.
Integrating Patient Experiences and the Role of Informed Consent
An often overlooked aspect of managing complicated medical conditions, especially those prevalent with confusing bits in diagnostic reports, is the patient experience. For individuals facing diagnostic uncertainty and potential surgical interventions, the emotional and psychological burden can be as significant as the physical challenges.
In situations where a lesion could either be a benign disorder such as Castleman’s disease or a malignancy, sharing the full scope of the diagnostic process becomes key. Patients must be fully informed of the possibilities, the steps involved, and the expected outcomes. This is not only a matter of legal necessity through informed consent but also a critical component of holistic care. Here are some strategies to improve patient communication:
- Clear Explanations: Use layman’s terms to describe the condition, the role of each diagnostic test, and what the results might imply. Avoid overly technical language that might obscure the fine details of the situation.
- Visual Aids: Diagrams, charts, and imaging examples can help patients visualize the location and nature of the lesion, making it easier for them to understand why certain tests or procedures are necessary.
- Emotional Support: Integrate counseling services within the care team to help patients manage anxiety and stress. Knowing that their concerns are acknowledged can make the overall process less intimidating.
By centering patient experiences in the diagnostic and treatment processes, physicians can foster a sense of trust and shared responsibility. This approach not only demystifies the complex parts of diagnosis but also helps patients feel more secure in taking charge of their healthcare journey.
Conclusion: Bridging Diagnostic Gaps and Embracing Holistic Care
The case of oesophageal unicentric Castleman’s disease offers a profound lesson in the unpredictable twists and turns of modern oncology. From misleading imaging results that point to malignancy to the definitive role of surgical intervention in obtaining a correct diagnosis, this case encapsulates the challenges clinicians face and the strategies they must adopt to deliver optimal care.
In our current healthcare environment, where technology and diagnostic tools continue to advance, it remains critical to remember that each patient represents a unique interplay of symptoms, imaging nuances, and clinical findings. This case teaches us the importance of comprehensive diagnostics, multidisciplinary collaboration, and the integration of alternative therapies and nutritional support as super important components of overall patient care.
As we move forward, ongoing research and clinical trials promise to shine more light on the hidden complexities of rare disorders like Castleman’s disease. Whether it is through improved genetic profiling, advanced imaging modalities, or more refined surgical techniques, the future of personalized medicine holds immense potential to reduce the nerve-wracking uncertainty that currently accompanies these challenging cases.
Ultimately, the journey through such a diagnostic maze is a team effort. It involves not only the combined expertise of specialists but also the active participation and informed consent of patients. By embracing both modern and alternative approaches, the medical community can continue to make significant strides in bridging diagnostic gaps and ensuring that each patient receives the care they deserve—a path that is as clear and supportive as it is innovative and evidence-based.
With cases like this as a guide, it is my belief that the future of healthcare will be marked by a thoughtful synthesis of rigorous scientific inquiry, empathetic patient care, and comprehensive treatment strategies that consider every side of the medical equation. In a landscape where every diagnostic step can be loaded with issues, the ability to figure a path through the maze is nothing short of essential.
Originally Post From https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/oncology/articles/10.3389/fonc.2025.1675203/abstract
Read more about this topic at
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis: an uncommon diagnostic …
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis: an uncommon diagnostic …